巨噬细胞在免疫和非免疫防御机制中起着重要作用,它们构成了防止细菌、病毒和其他形式的微生物污染侵入脊椎动物体内的第一道防线。巨噬细胞是一种大型细胞,几乎存在于所有身体组织中,它们可以具有不同的形式和名称(例如库普弗细胞、肺泡巨噬细胞、小胶质细胞、破骨细胞、红髓巨噬细胞)。 巨噬细胞“清除”,它们摄入并消化所有可能是潜在病原体的外来物质、微生物、癌细胞和细胞碎片,这个过程称为吞噬作用。 巨噬细胞主要通过可溶性分子(如细胞因子和趋化因子)的介导来进一步调节许多非吞噬细胞的功能。 它们参与先天性免疫、适应性免疫,并具有(抗)炎症作用。
Liposomes are artificially prepared spheres and consist of concentric phospholipid bilayers. When phospholipids are dispersed in water, the hydrophilic heads will make up both outer parts of the liposome, whereas the hydrophobic fatty acid groups will make up the inner part (see figure 1). Aqueous compartments separate the bilayers, and hydrophilic molecules can be dissolved in it, resulting in liposome-encapsulated molecules. Clodronate (dichloromethylene-bisphosphonate or Cl2MBP) is a hydrophilic molecule that can be encapsulated within phospholipid bilayers. Free clodronate does not easily cross cell membranes, and is rapidly cleared (i.e. within minutes) from circulation by the renal system. However, when entrapped in a liposome, the clodronate liposome is ingested by macrophages and cannot escape it (see figure 2). The phospholipid bilayers are digested by lysosomal phospholipases, whereas clodronate is not digested and remains in the macrophage. The more phospholipid bilayers and liposomes are ingested by the macrophage, the more clodronate will accumulate within the macrophage. Exceeding a certain intracellular concentration, clodronate will eliminate the macrophage by initiating its programmed cell death, i.e. apoptosis.
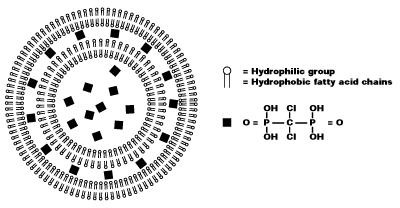
Figure 1. Schematic representation of a clodronate liposome. The vesicle consists of concentric phospholipid bilayers, separated by aqueous compartments. The bilayers consist of a hydrophilic and hydrophobic group. Clodronate (represented here as black squares) are dissolved in the aqueous solution and encapsulated within the liposome.
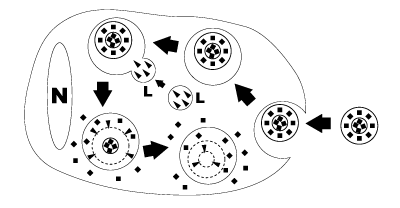
Figure 2. Schematic representation of clodronate liposome ingestion and digestion by a macrophage. Clodronate liposomes are ingested by the macrophages via endocytosis and then fused with the lysosomes (L) which contain phospholipases (arrowheads). The more phospholipid bilayers are disrupted by the phospholipases, the more clodronate (black squares) is released within the macrophage. Macrophages are ultimately killed through apoptosis. (N = nucleus of macrophage).
Thus, clodronate liposomes can be used to study macrophage functioning by depletion of macrophages. For instance, they can be applied in various models of autoimmune disease, transplantation, neurological disorders and gene therapy. Clodronate liposomes are only able to deplete macrophages if they can be reached. Some tissues can form barriers for the liposomes. By choosing the right administration route of clodronate liposomes, particular organs or tissues can be depleted of macrophages. For more information about administration protocols, click here.
PBS liposomes are mostly used for control experiments. However, these too can block phagocytosis by saturation for certain periods of time. PBS liposomes thus do not represent a control experiment with normal healthy, non-blocked, non-suppressed and non-activated macrophages. When comparing effects of clodronate liposomes with PBS liposomes, the effects can therefore be less than expected.
For more information, see:
– Van Rooijen, N., & Sanders, A. (1994). Liposome mediated depletion of macrophages: mechanism of action, preparation of liposomes and applications. Journal of immunological methods, 174(1-2), 83-93.
– Van Rooijen, N., Sanders, A., & van den Berg, T. K. (1996). Apoptosis of macrophages induced by liposome-mediated intracellular delivery of clodronate and propamidine. Journal of immunological methods, 193(1), 93-99.